In urban planning, real estate development, and architectural design, every inch matters. Whether you’re calculating how much floor space can be built on a given plot or determining how many risers to include in a stairway, precision is key. That’s where tools like the floor area ratio calculator come in.
But a well-designed building isn’t only about area—accessibility, layout, and compliance with building codes also rely on detailed calculations. Enter essential tools like the stair calculator, stair stringer calculator, and stair angle calculator. These ensure that structural designs are not only efficient but safe and functional.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to combine the floor area ratio calculator with modern stair calculators for a smarter, compliant, and more efficient approach to construction planning.
🏗️ What Is Floor Area Ratio (FAR)?
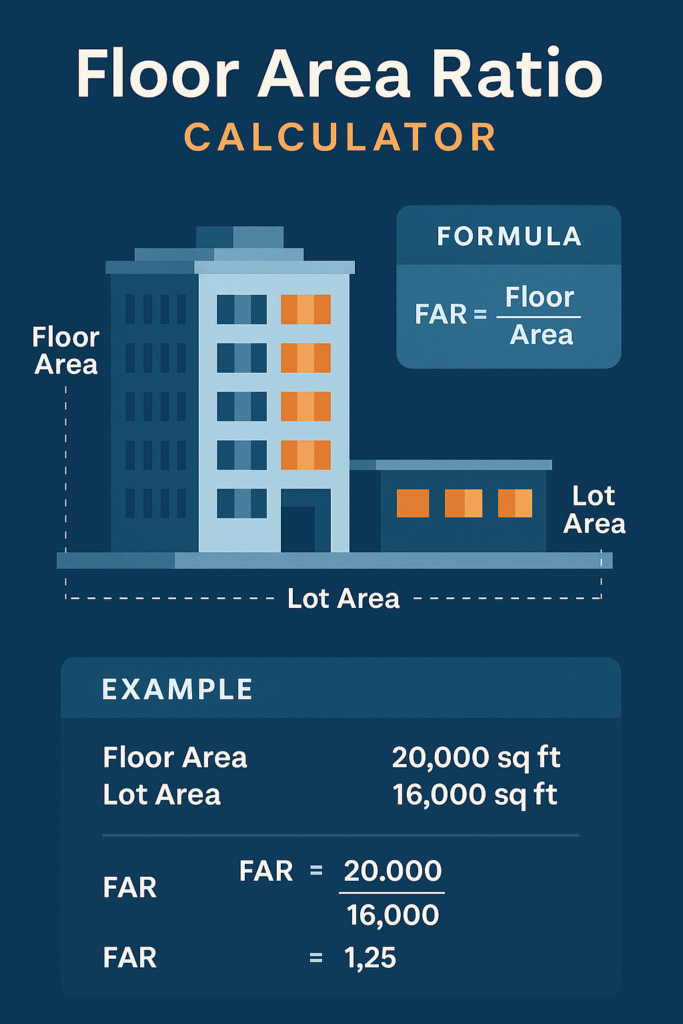
Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is a zoning regulation metric that describes the relationship between the total floor area of a building and the size of the plot of land on which it is built.
🔢 FAR Formula:
FAR=Total Floor AreaLot AreaFAR = \frac{\text{Total Floor Area}}{\text{Lot Area}}FAR=Lot AreaTotal Floor Area
✅ Example:
If you have a 2,000 sq ft lot and build a total of 5,000 sq ft across all floors, your FAR is: 50002000=2.5\frac{5000}{2000} = 2.520005000=2.5
This ratio tells planners how dense a development can be. Higher FARs are typical in city centers, while suburban or residential zones have lower FARs to preserve open space.
🛠 Why Use a Floor Area Ratio Calculator?
Manually calculating FAR can be time-consuming and error-prone, especially when dealing with:
- Multiple floors
- Partial basements
- Varying lot shapes
- Setback constraints
A floor area ratio calculator simplifies these tasks by automating input and ensuring zoning compliance in seconds.
How FAR Affects Building Design
FAR influences everything from how tall a building can be to how many residential units or commercial spaces it can include. Architects and developers use it to determine:
- Maximum buildable space
- Height restrictions
- Number of floors
- Open space requirements
- Fire access and stairwell planning
Which brings us to an often-overlooked consequence: staircase design.
🧱 Staircases and FAR: The Hidden Link
Staircases are more than passageways—they occupy floor area. Depending on your jurisdiction, staircases may or may not count toward FAR calculations. Regardless, their dimensions are critical for:
- Space planning
- Emergency egress compliance
- Accessibility
- Aesthetic balance
This is where the stair calculator, deck stair calculator, and stair stringer calculator come into play.
📐 Using a Stair Calculator in Your Building Plan
The stair calculator determines all major stair dimensions:
- Step height (riser)
- Step depth (tread)
- Total rise
- Total run
- Stair angle
- Stringer length
📏 Example:
Let’s say your building has a 10-foot floor height (120 inches). You want comfortable 7.5-inch risers and 10-inch treads.
Step-by-Step:
- Number of Risers = 120 ÷ 7.5 = 16
- Total Run = (16 – 1) × 10 = 150 inches
- Stringer Length = √(120² + 150²) = 192.09 inches
- Stair Angle = tan⁻¹(120 / 150) ≈ 38.66°
These values are essential for both safety and FAR efficiency. Oversized stairs take up usable area, while undersized ones can violate code.
🪜 Stair Stringer Calculator: Structural Integrity First
The stair stringer calculator focuses on the load-bearing component of a staircase—the stringer.
Stringers are the diagonal boards that support the treads and risers. You typically need:
- 2 stringers for a narrow stair
- 3+ for wider stairs (36″ or more)
The calculator determines:
- Cut angles
- Run and rise per step
- Material length required
It ensures your stair design remains safe without wasting valuable material that could affect your FAR build-out plan.
🧠 Stair Angle Calculator: Optimizing Space and Comfort
Stair angles typically range between 30° and 40°. The stair angle calculator ensures the angle is:
- Comfortable to walk
- Meets local codes
- Doesn’t encroach into headroom
Too steep, and you risk non-compliance. Too shallow, and stairs may take up more floor area—impacting your floor area ratio calculator output.
📊 Total Rise and Run: Calculated with Precision
Use the calculate stair rise and run tool to:
- Determine number of steps
- Calculate headroom
- Align floor-to-floor heights
- Design landings and mid-stairs efficiently
Efficient stair placement can reduce wasted space and free up more buildable floor area, increasing your usable FAR.
🔄 Deck Stair Calculator: Exterior Access Planning
Not all stairs are internal. The deck stair calculator is useful when planning exterior or emergency stairs, especially for buildings with:
- Rooftop decks
- Terraced designs
- Multiple building entrances
Each of these external staircases should be planned carefully to avoid compromising the total FAR or encroaching into setback areas.
📥 Example Table: FAR and Stair Calculation Summary
| Calculation Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Floor Area Ratio (FAR) | FAR = Total Floor Area / Lot Area | 5000 sq ft / 2000 sq ft = 2.5 |
| Stair Stringer Length | √(Rise² + Run²) | √(120² + 150²) = 192.09 in |
| Stair Angle | tan⁻¹(Rise / Run) | tan⁻¹(120 / 150) ≈ 38.66° |
| Step Height | Total Rise / Number of Steps | 120 / 16 = 7.5 in |
| Total Run | Tread Depth × (Number of Steps – 1) | 10 × 15 = 150 in |
📏 Step Height Calculator vs Stair Tread Calculator
These tools help you fine-tune stair dimensions:
- Step Height Calculator: Ensures riser height consistency
- Stair Tread Calculator: Calculates tread depth based on comfort and code
Their values directly affect stair dimensions, which indirectly shape FAR-based design layout.
🧮 Calculate Stringer Length with Ease
The calculate stringer length tool helps prevent framing mistakes. It accounts for:
- Total rise and run
- Tread thickness
- Lumber type
Efficient stringer planning helps optimize wood use and keeps staircases from becoming space hogs, maximizing your floor area ratio calculator performance.
🔄 Staircase Calculator: All-in-One Design Tool
The staircase calculator brings it all together, calculating:
- Step count
- Total height
- Run length
- Headroom clearance
- Rail angle
- Stringer requirements
When paired with the floor area ratio calculator, it ensures your designs are space-smart and code-compliant.
🏙️ Urban Planning and Zoning with FAR
Local municipalities use FAR to:
- Limit building density
- Ensure daylight, ventilation, and green space
- Protect neighborhood character
- Support infrastructure capacity
A floor area ratio calculator helps architects comply while maximizing usable space—especially important in urban infill or redevelopment projects.
💡 Pro Tip: Use Both Tools Side by Side
- Start with FAR Calculator
- Determine total floor area allowed
- Lay Out Stairs with Calculators
- Use stair calculator, stair stringer calculator, and stair angle calculator
- Fit stairs efficiently within the footprint
- Optimize Floor Plan
- Align with zoning rules, height limits, and FAR constraints
- Recalculate as Needed
- Adjust stair slope or landings if needed to save space
This approach ensures you use your land and building envelope as efficiently as possible.
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring stair impact on FAR
- Assuming all stairs are excluded from FAR (varies by code)
- Overbuilding stairs and reducing usable space
- Not planning for landings and handrails
- Miscalculating tread/riser ratios leading to code violations
🧠 Final Thoughts: Build Smarter with Accurate Calculators
Success in architecture and construction hinges on accuracy and compliance. By using tools like the floor area ratio calculator, stair calculator, deck stair calculator, and stair stringer calculator, you:
- Stay within code
- Maximize buildable space
- Design more efficiently
- Reduce errors and rework
From multi-family housing to commercial developments, the right calculators save you time, money, and headaches.