Free Building Occupancy Calculator Online
Calculating building occupancy is a critical step in ensuring the safety, functionality, and compliance of any commercial or residential structure. Whether you’re designing a new office, reviewing fire code compliance for a school, or planning for maximum capacity at an event venue, a building occupancy calculator simplifies the process. This tool uses mathematical formulas and code-based guidelines to determine how many individuals can safely occupy a space based on room size, function, and exit availability. Tools like Construction Calculators make it easier to stay compliant and accurate during planning.
This guide explains what a building occupancy calculator is, why it matters, and how it uses industry-standard formulas and occupancy factors to produce reliable results.
Building Occupancy Calculator
What Is a Building Occupancy Calculator?
A building occupancy calculator is a digital tool or manual method used to estimate the maximum occupancy of a room or entire structure. It takes into account the usable floor area, intended use of the space, and occupancy load factors as defined in codes such as the International Building Code (IBC) or NFPA Life Safety Code.
Occupancy limits are not arbitrary—they exist to safeguard the health and safety of all occupants. A space that is over-occupied can present serious risks in emergencies like fires or earthquakes. Exceeding occupancy limits can also lead to building code violations, fines, and liability in the event of an incident.
Why Accurate Occupancy Calculations Matter
Accurate building occupancy calculations serve several purposes across industries:
- Ensure compliance with building and fire codes
- Prevent overcrowding and minimize emergency evacuation risks
- Aid in space planning and design decisions
- Establish safe limits for events and public spaces
- Provide data for HVAC and ventilation system sizing
- Assist in facility management and legal documentation
A properly calculated occupancy load promotes safety, function, and legal compliance.
Factors That Affect Occupancy Load
Building occupancy calculations rely on multiple inputs. The most common include:
- Use classification (e.g., office, assembly, classroom, residential)
- Room or floor area (measured in square feet or square meters)
- Occupant load factor (standard value depending on use)
- Exits and egress width
- Furniture or fixed seating layout
The calculator applies these variables to code-defined formulas to determine a safe and functional occupant load.
How to Calculate Occupancy – The Formula
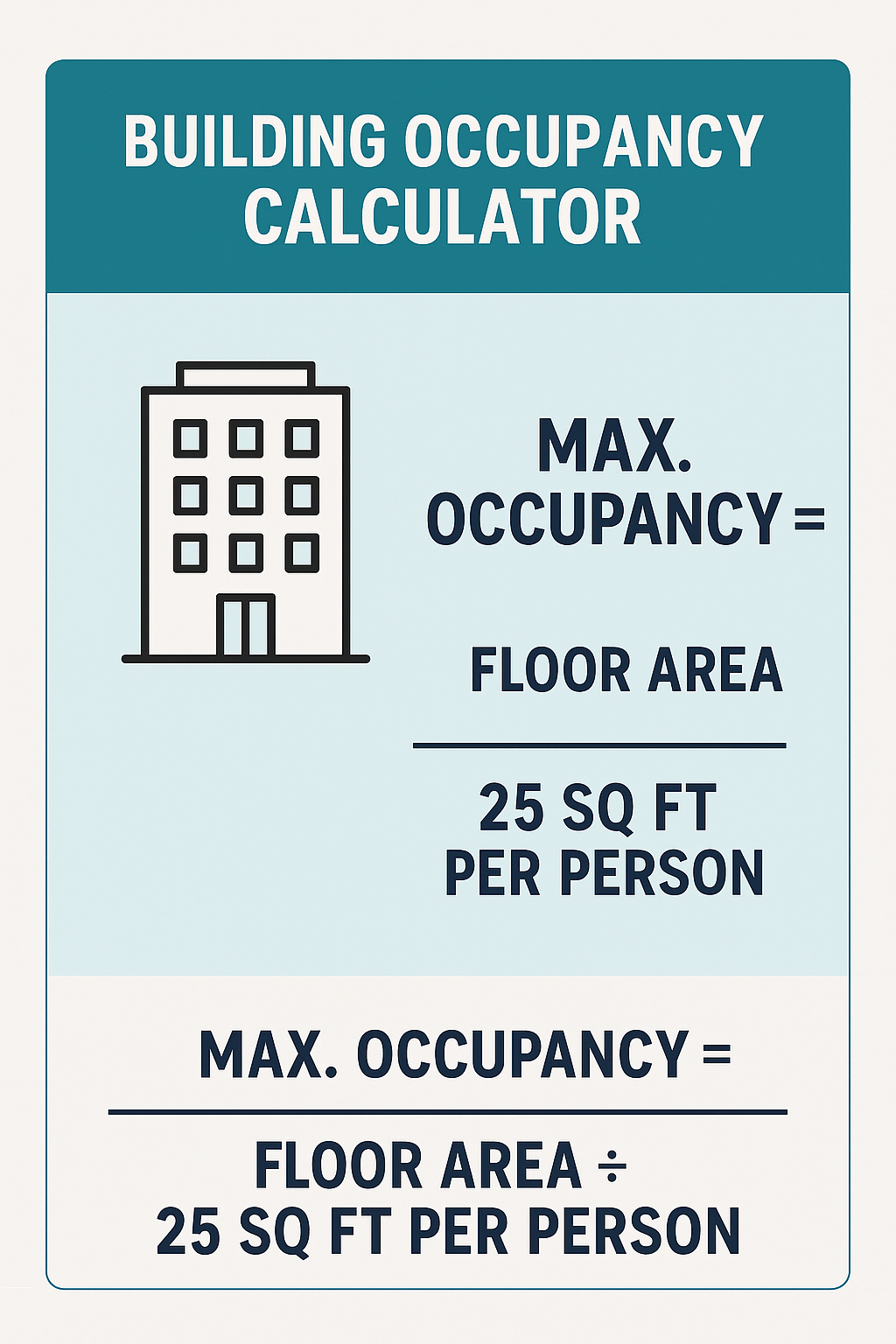
The basic formula used by a building occupancy calculator is: $$Occupancy Load=Floor AreaOccupant Load Factor\text{Occupancy Load} = \frac{\text{Floor Area}}{\text{Occupant Load Factor}}Occupancy Load=Occupant Load FactorFloor Area$$
Where:
- $$Floor Area\text{Floor Area}Floor Area = Usable space in square feet (ft²)$$
- $$Occupant Load Factor\text{Occupant Load Factor}Occupant Load Factor = Area per person (ft²/person) based on use classification$$
These load factors are generally defined in the IBC. For example:
| Use Type | Load Factor (ft²/person) |
|---|---|
| Office | 100 |
| Classroom | 20 |
| Assembly (chairs) | 7 |
| Retail | 30 |
| Industrial | 100 |
| Restaurant | 15 |
Example:
If a restaurant dining area is 1,200 square feet:$$ Occupancy Load=120015=80 people\text{Occupancy Load} = \frac{1200}{15} = 80 \text{ people}Occupancy Load=151200=80 people$$
Advanced Considerations: Egress Capacity
In addition to floor area and use, occupancy calculations often include egress capacity, or how many people can safely exit during an emergency. $$Maximum Egress Capacity=∑(Exit Width (in)Required Width Per Person (in/person))\text{Maximum Egress Capacity} = \sum \left( \frac{\text{Exit Width (in)}}{\text{Required Width Per Person (in/person)}} \right)Maximum Egress Capacity=∑(Required Width Per Person (in/person)Exit Width (in))$$
Typical egress width requirements per person:
- Stairways: 0.3 inches/person
- Other exits: 0.2 inches/person
Example:
A building with two stairways, each 60 inches wide: $$Egress Capacity=600.3+600.3=200+200=400 people\text{Egress Capacity} = \frac{60}{0.3} + \frac{60}{0.3} = 200 + 200 = 400 \text{ people}Egress Capacity=0.360+0.360=200+200=400 people$$
In this case, the building must not exceed the lower of the two calculations (floor-based load vs. egress capacity).
Using a Building Occupancy Calculator: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Measure the Floor Area
Use a tape measure or architectural plan to determine the total usable space. Do not include restrooms, storage areas, or walls unless they are part of the primary use.
Step 2: Identify the Room Use
Select the occupancy classification that fits the space’s function: office, classroom, assembly, dining, etc.
Step 3: Apply Load Factors
Refer to the latest code standards for occupancy load factors.
Step 4: Run the Formula
$$Occupancy Load=AreaLoad Factor\text{Occupancy Load} = \frac{\text{Area}}{\text{Load Factor}}Occupancy Load=Load FactorArea$$
Round down to the nearest whole person unless the code specifies otherwise.
Step 5: Confirm Egress Capacity
$$Exit Capacity=0.2Exit Width(or 0.3Exit Width for stairways)$$
Make sure the exit capacity supports the calculated occupancy.
Occupancy Code References
Most occupancy calculators follow:
- International Building Code (IBC)
- NFPA 101: Life Safety Code
- Local amendments or state-specific regulations
It’s critical to check the local jurisdiction’s code requirements before applying any calculated results in construction or design.
Occupancy Planning for Different Spaces
Office Buildings
These are generally assigned a load factor of 100 ft²/person. Commonly include shared exits and must comply with ADA egress paths.
Classrooms
K–12 classrooms are typically calculated at 20 ft²/person. Higher education may differ based on room setup.
Assembly Spaces
Includes theaters, churches, gyms, and restaurants. May use 7 ft²/person without tables or 15 ft²/person with seating.
Residential Buildings
Calculated per dwelling unit or by bedroom count, depending on code.
Industrial and Storage
Usually assigned a high load factor (e.g., 300 ft²/person), with consideration for machinery, racks, and limited foot traffic.
Common Pitfalls in Occupancy Calculations
- Using gross area instead of usable area
- Ignoring egress limitations
- Failing to update for renovations or layout changes
- Not considering mezzanines or lofts
- Assuming fire marshal will approve unofficial estimates
Accurate input leads to compliant output. Mistakes can delay inspections, permit approvals, and occupancy certificates.
Benefits of Using a Digital Calculator
- Fast and repeatable calculations
- Updates based on new code cycles
- Built-in occupancy factor tables
- Integration with fire safety and HVAC planning
- Exportable reports for planning and approval
Browser-based occupancy calculators use JavaScript and responsive interfaces, making them accessible on-site or in the office.
Final Summary: Know Your Safe Limits
A building occupancy calculator helps professionals, developers, and facility managers ensure that spaces are used legally and safely. These tools save time, reduce risk, and keep projects compliant with evolving building codes.
By understanding the formulas, load factors, and egress limitations, you can create a space that meets safety standards and serves people well whether it’s a bustling office, a school auditorium, or a warehouse.
Conclusion
Accurate occupancy calculation is more than just a number—it’s a vital part of responsible design and code compliance. Whether you’re building a new facility, renovating an old one, or hosting an event, the building occupancy calculator ensures you stay within safe and legal limits. With a clear grasp of floor area, occupant load factors, and egress requirements, you can confidently plan for safety and efficiency using tools like General Construction Calculators, construction calculator osrs, and the Taper Calculator.
Use the calculator before submitting permit applications, organizing large gatherings, or designing new layouts. With each calculation, you take one more step toward safety, order, and readiness in every building you manage or design.
