Free Drainage Slope Calculator Online
A drainage slope calculator is an essential tool for determining the correct incline needed to effectively move water away from structures, foundations, and landscapes. Whether you’re designing a residential yard, grading for a driveway, or installing stormwater pipes, using Construction Calculators ensures you calculate the correct slope to maintain proper water flow, prevent pooling, and protect your property from water damage.
In both small DIY projects and large civil engineering jobs, slope or grade is what determines how well your drainage system performs.
Drainage Slope Calculator
What Is Drainage Slope?
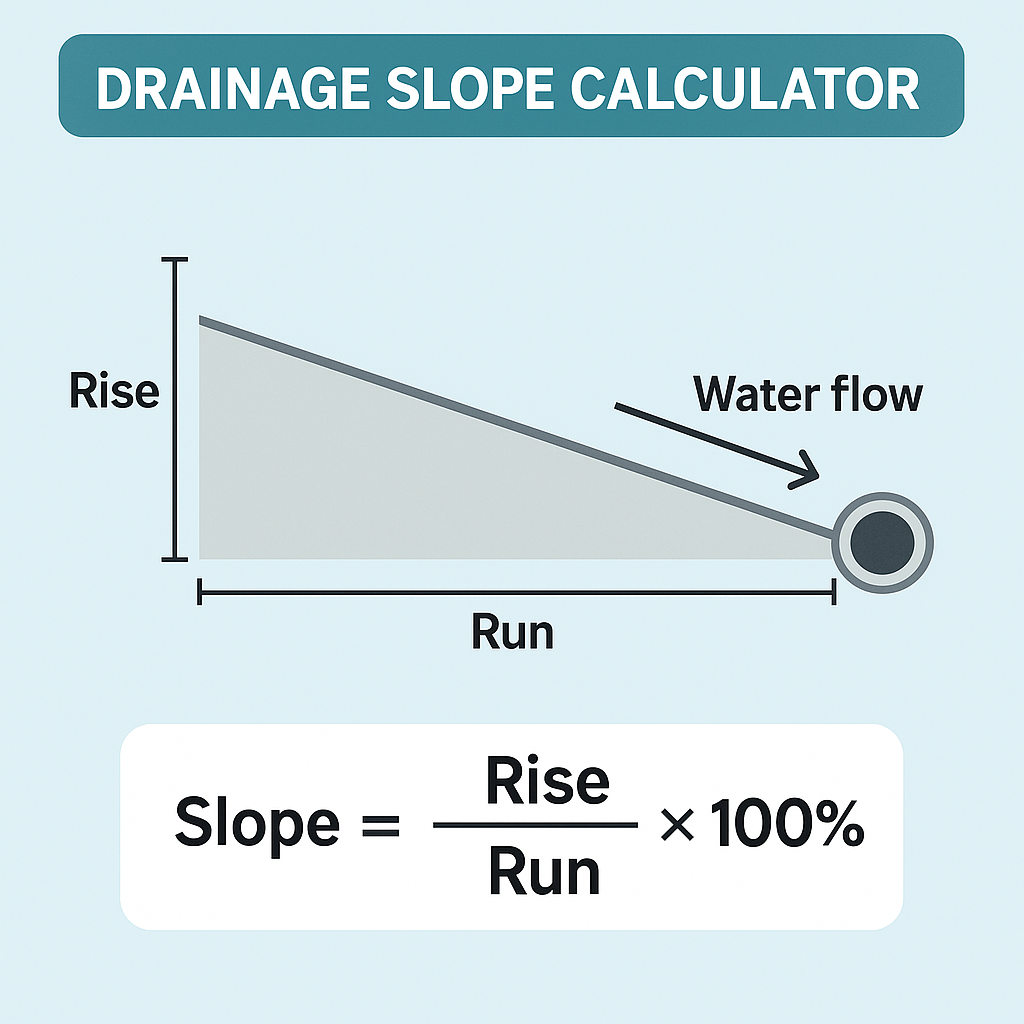
Drainage slope, or grade, refers to the vertical drop over a horizontal distance. It is usually expressed as a percentage or ratio and ensures gravity moves water in the desired direction. For example, a slope of 1% means the ground drops 1 unit vertically for every 100 units horizontally.
Poor slope design can lead to:
- Standing water
- Soil erosion
- Foundation damage
- Flooding
Using a drainage slope calculator simplifies the design process and ensures your project meets building standards and practical drainage requirements.
Why Is Drainage Slope Important?
Proper slope helps you:
- Channel stormwater away from buildings
- Prevent foundation leaks and erosion
- Ensure compliance with building codes
- Design effective stormwater and sewer lines
- Improve lawn and landscape health
The minimum slope often recommended for lawns or hardscaping is 2%, while drainage pipes typically require a slope between 1% and 2%.
Basic Drainage Slope Formula
To calculate slope manually, use this basic equation: $$Slope (%)=(Rise (vertical change)Run (horizontal distance))×100\text{Slope (\%)} = \left( \frac{\text{Rise (vertical change)}}{\text{Run (horizontal distance)}} \right) \times 100Slope (%)=(Run (horizontal distance)Rise (vertical change))×100$$
Where:
- Rise = Difference in elevation (inches or feet)
- Run = Horizontal distance over which that change occurs
You can also express this as a decimal or ratio: $$Slope (decimal)=RiseRun\text{Slope (decimal)} = \frac{\text{Rise}}{\text{Run}}Slope (decimal)=RunRise$$
Example: Calculating Lawn Drainage Slope
Let’s say you want to grade your yard away from the foundation for proper drainage.
- Distance from house: 10 feet
- Desired slope: 2%
Apply the formula: $$Rise=2100×10=0.2 ft (or 2.4 inches)\text{Rise} = \frac{2}{100} \times 10 = 0.2 \text{ ft (or 2.4 inches)}Rise=1002×10=0.2 ft (or 2.4 inches)$$
So, your yard should slope 2.4 inches downward over a 10-foot distance.
Drainage Slope Calculator Inputs
A standard drainage slope calculator will typically ask for:
- Start elevation (in feet or meters)
- End elevation
- Total horizontal distance
- Desired slope percentage (optional)
The calculator then returns:
- Rise
- Slope (%)
- Whether the slope meets recommended guidelines for drainage
These tools simplify grading and trench planning for homeowners, landscapers, and engineers.
Pipe Drainage and Sewer Design
In stormwater and sewer system design, maintaining the proper slope is vital. Too steep a slope can cause erosion; too shallow a slope can cause clogging.
Minimum Slopes for Drainage Pipes:
- 4-inch pipe: 1% (or 1/8″ per foot)
- 6-inch pipe: 0.5%
- 8-inch pipe: 0.33%
Formula for pipe slope: Required Fall=$$Run×Slope\text{Required Fall} = \text{Run} \times \text{Slope}Required Fall=Run×Slope$$
For example, if a 4-inch pipe runs for 100 feet: $$Fall=100×0.01=1 foot\text{Fall} = 100 \times 0.01 = 1 \text{ foot}Fall=100×0.01=1 foot$$
So the pipe should drop 1 foot over the 100-foot run.
Types of Drainage Where Slope Matters
1. Surface Drainage
Includes lawns, sidewalks, and driveways. Typical slope: 2% to 5%.
2. Subsurface Drainage
French drains or trench systems beneath the soil. Minimum slope: 1%.
3. Roof Drainage
Flat roofs often use internal drains that require at least 1/8 inch per foot.
4. Foundation Grading
To move water away from foundations, aim for 6 inches of fall within the first 10 feet.
Slope Conversion Table
| Slope (%) | Inches per Foot | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5% | 1/16″ | 1:200 |
| 1% | 1/8″ | 1:100 |
| 2% | 1/4″ | 1:50 |
| 5% | 5/8″ | 1:20 |
Use these conversions when evaluating slope using manual tools like levels or tape measures.
Common FAQs
Q1: What’s the ideal slope for residential drainage?
Aim for at least 2% for surface grading and 1% for drainage pipes.
Q2: Can I use this calculator for French drains?
Yes. Enter your trench length and desired fall. Ensure you maintain at least 1 inch per 10 feet.
Q3: Is slope the same as grade?
Yes, both terms refer to the same concept—vertical change over a horizontal run.
Q4: How do I measure slope in the field?
Use a line level, laser level, or string and tape. Then plug in rise/run values into the drainage slope calculator.
Q5: Is too much slope bad?
Yes. It can cause erosion and pipe scouring, especially in sewer systems.
Real-World Applications
Landscaping Projects
Design swales and plant beds that channel water safely without pooling.
Home Construction
Ensure proper grading to prevent water damage to basements and crawl spaces.
Driveway and Road Grading
Avoid standing water and frost heaves by maintaining a minimum 2% slope.
Rainwater Systems
Plan gutter and downspout drains with sufficient slope to avoid overflow or backup.
Final Thoughts
A drainage slope calculator is more than just a number-crunching tool—it’s a practical solution to one of the most important aspects of site design and water management. Whether you’re installing a new pipe, grading a lawn, or managing stormwater runoff, calculating slope properly prevents future headaches, costly repairs, and safety issues. Tools like the General Construction Calculators, Tank Volume Calculator, and Stair Calculator ensure accurate results and smooth drainage system planning.
By using simple formulas like: $$\text{Slope (\%)} = \left( \frac{\text{Rise}}{\text{Run}} \right) \times 100$$
you ensure water flows in the right direction, at the right rate, for the right results.
