Free Elevation Grade Calculator Online
In both engineering and everyday life, understanding elevation grade is essential. Whether you’re designing roads, climbing a trail, or planning a construction project, you need to calculate how steep a surface is. That’s where the Elevation Grade Calculator comes Construction Calculators, it is a tool that translates changes in elevation into practical data like slope, percentage, angle, and distance.
This guide explains the math behind it, provides real-world examples, and walks you through using an elevation grade calculator for everything from measuring elevation gain on a hiking route to managing ground slope in large-scale engineering projects.
Elevation Grade Calculator
What Is Elevation Grade?
Elevation grade (also called slope, incline, or grade percentage) describes the steepness of a surface over a specific horizontal distance. It’s typically expressed as a percentage or angle and is essential in fields like:
- Construction
- Road design
- Hiking trail planning
- Engineering
- Land surveying
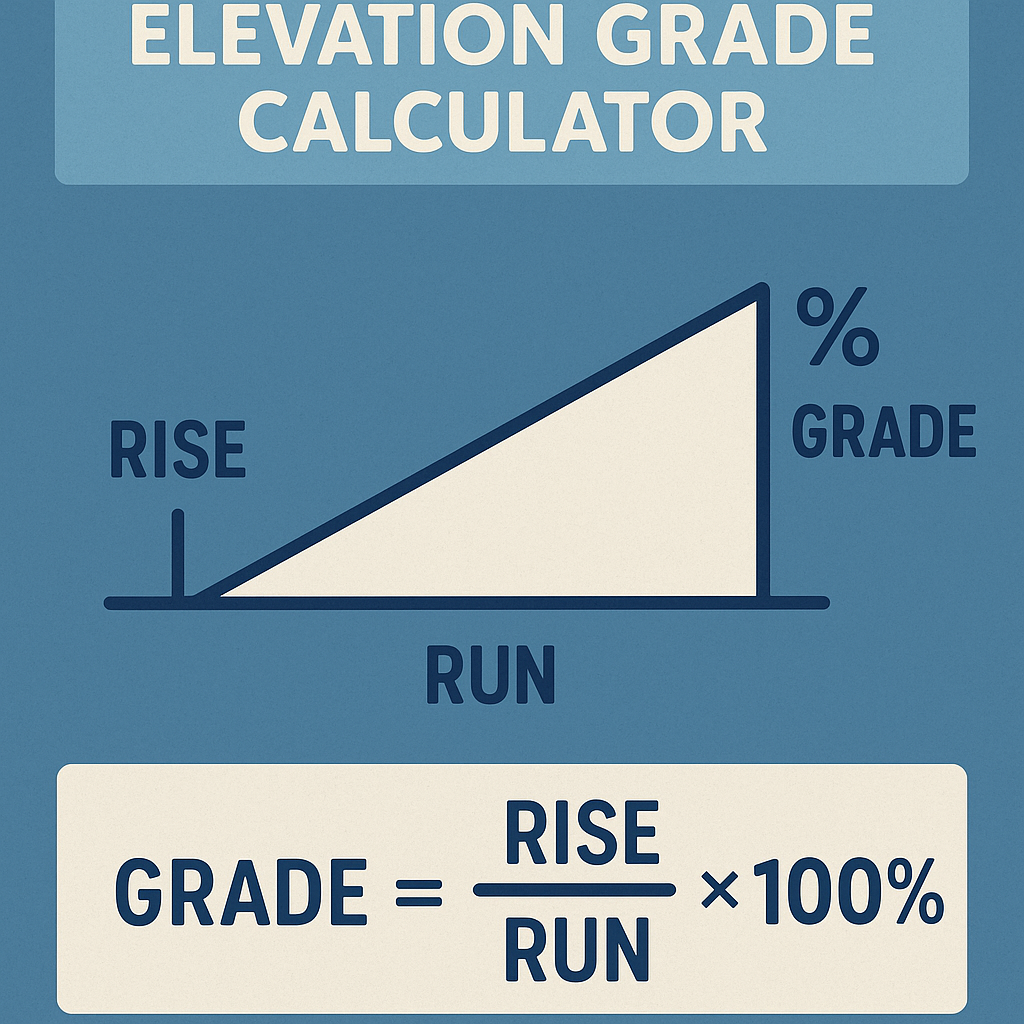
Elevation Grade Formula
Grade (%)=$$(Horizontal RunVertical Rise)×100$$
Where:
- Vertical Rise = Change in height or elevation
- Horizontal Run = Ground-level distance
- Both must be in the same unit (feet, meters, etc.)
Example Calculation
Let’s say you climbed a hill with:
- Elevation gain = 30 feet
- Horizontal distance = 200 feet
$$[
\text{Grade (\%)} = \left( \frac{\text{Total Marks Obtained}}{\text{Total Marks}} \right) \times 100
]$$
$$[
\text{Grade (\%)} = \left( \frac{30}{200} \right) \times 100 = 15\%
]$$
This means for every 100 feet of horizontal travel, you climb 15 feet in vertical distance a fairly steep grade often found on hiking trails or challenging road segments.
Why Use an Elevation Grade Calculator?
Manual calculations can be time-consuming, especially when dealing with complex terrains or engineering data. A digital elevation grade calculator streamlines this process by:
- Accepting distance, elevation, and unit inputs
- Automatically calculating slope, angle, and percentage
- Providing results in feet, meters, degrees, or percent grade
- Ensuring data consistency across multiple points or trail sections
Inputs You Need
| Input Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Vertical Rise | Change in elevation or height |
| Horizontal Run | Ground distance traveled |
| Units | Must use the same unit (feet, meters) |
| Measurement Tools | Leveling rod, survey equipment, measuring tape |
You can also use GPS tools, mobile apps, or map data for more advanced grade calculations.
Units & Conversions
| From | To | Multiply By |
|---|---|---|
| Meters to Feet | Feet | 3.28084 |
| Feet to Meters | Meters | 0.3048 |
| Degrees to Percent Grade | % | tan(θ)×100\tan(\theta) \times 100tan(θ)×100 |
| Percent Grade to Degrees | Degrees | arctan(%)\arctan(\%)arctan(%) |
Always ensure you’re using the same measurement system throughout your elevation grade calculator input.
Applications in Construction and Engineering
1. Roads and Highways
Engineers must control grade slope to prevent slipping, especially in steep grades. Common road grades range from 4–10%.
2. Hiking Trails
Trail steepness affects physical challenge and energy expenditure. Steep trails with 15–20% grade are common in mountain regions.
3. Surveying and Mapping
Elevation gain across long horizontal distance is used in topographical maps and land development plans.
4. Architectural Design
Grading is used for site leveling, drainage systems, and foundation planning.
Grade as a Slope or Ratio
Sometimes grade is expressed as a ratio like 1:20, meaning 1 unit of rise for every 20 units of run.
To convert percentage grade to a ratio: $$Ratio=1(100Grade %)\text{Ratio} = \frac{1}{\left( \frac{100}{\text{Grade \%}} \right)}Ratio=(Grade %100)1$$
A 5% slope = 1:20
This is useful for accessibility standards (e.g., ADA-compliant ramps).
Energy and Effort on Trails
Climbing a steep slope increases energy use. Use this data to:
- Plan rest stops
- Estimate caloric burn
- Determine trail difficulty level
In engineering, this helps estimate vehicle power requirements and fuel usage.
Common Grade Values Table
| Grade (%) | Angle (°) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 0° | Level surface |
| 5% | ~2.86° | Gentle incline |
| 10% | ~5.71° | Moderate incline |
| 15% | ~8.53° | Steep grade |
| 20% | ~11.31° | Very steep |
Use these reference points when interpreting results from an elevation grade calculator.
Calculating Elevation Gain
Sometimes, you need to determine total elevation gain across multiple points. For example, a hiking trail may climb and descend several times.
To calculate:
- Track each positive elevation change
- Ignore declines
- Sum all gains for total elevation gain
This is a critical metric in fitness apps and route planning software.
Angle vs Percentage
Both express slope, but:
- Angle (degrees) is better for engineering and design
- Percentage (%) is easier for public interpretation
Conversion Formula: $$Angle=arctan(RiseRun)\text{Angle} = \arctan\left(\frac{\text{Rise}}{\text{Run}}\right)Angle=arctan(RunRise)$$
Use a degrees calculator or scientific calculator to compute arctan values.
Real-World Use Case
Imagine you’re designing a wheelchair-accessible ramp:
- Max allowed grade is 8.33% (1:12)
- You have a vertical rise of 2 feet
Calculate needed horizontal distance: $$Run=RiseGrade %×100=28.33×100≈24feet\text{Run} = \frac{\text{Rise}}{\text{Grade \%}} \times 100 = \frac{2}{8.33} \times 100 ≈ 24 feetRun=Grade %Rise×100=8.332×100≈24feet$$
Your ramp needs to extend 24 feet to comply with code.
Tools to Assist You
- Leveling Rods
- GPS-based Survey Apps
- Laser Measurement Tools
- Elevation Grade Calculator (online or app-based)
- Trail Mapping Software
Use multiple tools for higher accuracy, especially in engineering projects or long-distance routes.
FAQs
Q: What does elevation percentage mean?
A: It shows how much height you gain over a horizontal distance, expressed as a %.
Q: What’s the steepest road in the world?
A: Baldwin Street in New Zealand, with a 35% grade slope.
Q: Can I use feet and meters in the same calculation?
A: No. Always use the same unit (e.g., feet or meters) for rise and run.
Q: What’s a good elevation gain for a moderate hike?
A: Around 500–1000 feet over 3–5 miles is considered moderate.
Final Thoughts
The Elevation Grade Calculator is an essential tool for anyone working with terrain, slopes, or elevation differences. Whether you’re planning a driveway, designing a trail, or preparing a construction site, this calculator delivers the accuracy you need. When used together with the ramp calculator, stair calculator, and other General Construction Calculators, it helps ensure your grading work is safe, compliant, and well-executed.
- Designing a construction site
- Planning a road
- Measuring hiking trail steepness
- Engineering drainage systems
this calculator delivers precise, fast, and useful outputs for smarter decision-making.
From decimal grade percentages to degrees, from trail planning to engineering measurements, it simplifies complex data into easy-to-understand numbers. Just plug in your vertical rise and horizontal run, choose your unit, and let the tool do the math.
Summary Table: Elevation Grade Calculator Inputs and Outputs
| Input | Unit Options | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Rise | Feet / Meters | Change in height |
| Horizontal Distance | Feet / Meters | Ground-level distance |
| Output – % Grade | Percentage | Rise over run as a percentage |
| Output – Angle | Degrees | Incline angle |
| Output – Ratio | 1:X | Unit ratio of rise to run |
