Free Pipe Volume Calculator Online
Accurate measurement is the foundation of every reliable plumbing, HVAC, or engineering system. Whether you’re calculating the water capacity in a pipeline, designing a fluid system, or estimating material for a cylindrical conduit, the Pipe Volume Calculator is your go-to tool. As part of the essential Construction Calculators, it provides accurate results for professionals and DIYers who need to know the volume, flow rate, or mass of the fluid a pipe can carry.
This guide explains the importance of pipe volume calculations, showcases the correct pipe volume formula, and walks through real-world examples using various units, from cubic inches to gallons.
Pipe Volume Calculator
What Is a Pipe Volume Calculator?
A pipe volume calculator is a tool designed to calculate the internal volume of a cylindrical pipe using measurements like inner diameter, length, and wall thickness. Whether you’re working in imperial units (inches, feet, gallons) or metric units (millimeters, meters, liters), this calculator adapts to your needs.
Key industries using this calculator include:
- Plumbing systems
- HVAC design
- Water treatment
- Engineering applications
- Material volume estimates
Why Pipe Volume Calculations Matter
Knowing a pipe’s volume helps you:
- Estimate fluid weight and mass
- Determine flow rates
- Design storage and transfer systems
- Understand pipe capacity
- Choose appropriate pipe material and pipe diameter
- Optimize duct sizing and liquid density control
Whether you’re designing a simple irrigation system or a complex industrial fluid network, a pipe volume calculator ensures efficiency and safety.
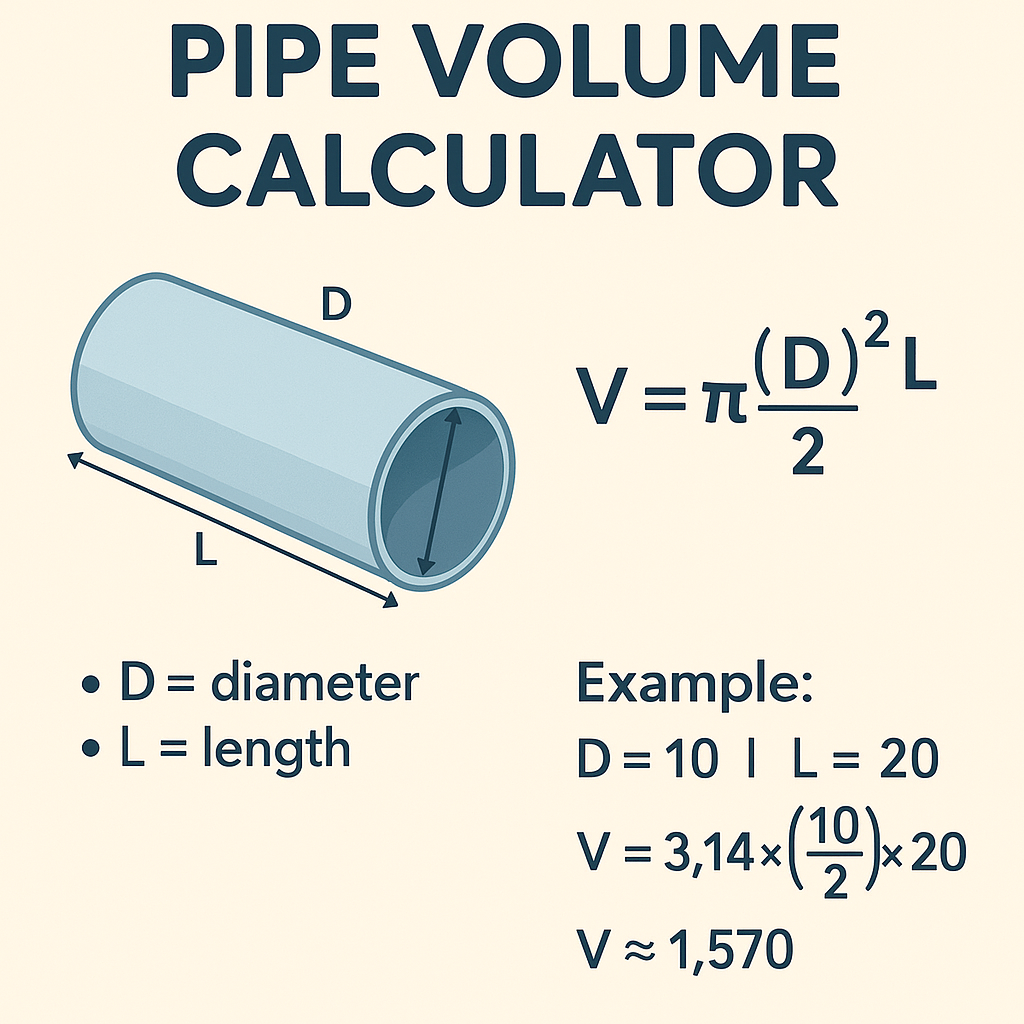
Pipe Volume Formula
To calculate the volume of a cylindrical pipe, use this standard pipe volume formula: $$Volume=π×(d2)2×L\text{Volume} = \pi \times \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 \times LVolume=π×(2d)2×L$$
Where:
- π\piπ ≈ 3.1416
- ddd = Inner diameter of the pipe
- LLL = Length of the pipe
This gives you volume in cubic units typically cubic inches, cubic feet, or cubic meters, depending on input.
Example Calculation
Let’s say you have a cylindrical pipe with:
- Inner diameter = 4 inches
- Length = 120 inches (10 feet)
$$Volume=π×(42)2×120=π×4×120=1,507.96 cubic inches\text{Volume} = \pi \times \left( \frac{4}{2} \right)^2 \times 120 = \pi \times 4 \times 120 = 1,507.96 \text{ cubic inches}Volume=π×(24)2×120=π×4×120=1,507.96 cubic inches$$
To convert to gallons: $$Gallons=1507.96231≈6.53 gallons\text{Gallons} = \frac{1507.96}{231} ≈ 6.53 \text{ gallons}Gallons=2311507.96≈6.53 gallons$$
This pipe volume calculation shows that the pipe can hold approximately 6.53 gallons of water or liquid.
Important Variables in Pipe Volume Calculations
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Pipe Length | Total length of the pipe (feet, meters, or inches) |
| Inner Diameter | Measurement from inside edge to inside edge |
| Pipe Radius | Half of the inner diameter |
| Wall Thickness | Used if only outer diameter is known |
| Flow Rate | Speed at which fluid passes through the pipe |
| Fluid Density | Helps calculate mass and weight |
| Units | Choose between cubic inches, feet, or meters |
Pipe Volume Calculator for Multiple Units
Most pipe volume calculators offer options for different units:
- Imperial Units: Cubic inches, cubic feet, gallons, pounds
- Metric Units: Cubic meters, liters, milliliters, kilograms
With the right unit conversion factors, you can easily move between measurement systems to suit your project.
Calculating Liquid Weight and Mass
Once you have volume, you can calculate liquid mass or water weight using fluid density: Mass=Volume×Density\text{Mass} = \text{Volume} \times \text{Density}Mass=Volume×Density
For example:
- Volume = 6.53 gallons
- Water density ≈ 8.34 lb/gallon
$$Mass=6.53×8.34≈54.44 pounds\text{Mass} = 6.53 \times 8.34 ≈ 54.44 \text{ pounds}Mass=6.53×8.34≈54.44 pounds$$
This is useful in determining load-bearing requirements, system pressure, and material capacity.
Application in Engineering and Design
1. Plumbing Systems
Used to size pipes for residential and industrial water systems to prevent under- or over-pressurization.
2. HVAC Ductwork
Accurate volume calculations assist in determining airflow rates, pipe size, and duct sizing requirements.
3. Water Tanks and Storage
Used to match pipe volume with tank volume to avoid overflow or supply issues.
4. Fluid Flow Systems
Ensures accurate calculations for flow rates, pipe resistance, and distribution systems.
Pipe Diameter vs Outer Diameter
To ensure accurate pipe volume, always use the inner diameter, not outer diameter.
If you only have the outer diameter and wall thickness, calculate inner diameter as: Inner Diameter=$$Outer Diameter−(2×Wall Thickness)\text{Inner Diameter} = \text{Outer Diameter} – (2 \times \text{Wall Thickness})Inner Diameter=Outer Diameter−(2×Wall Thickness)$$
This adjustment is crucial in pipe systems handling liquids, where even minor errors can affect flow rate or capacity.
Tips for Accurate Results
- Use calibrated tools for diameter and length measurement
- Always measure inner diameter
- Convert all units to be consistent (e.g., inches to feet)
- Double-check your unit conversion
- Use a pipe volume calculator with a flow rate feature if designing dynamic systems
Pipe Volume by Material Type
The pipe material (PVC, steel, copper, etc.) doesn’t change the internal volume calculation but affects:
- Weight
- Pressure resistance
- Durability
For mass flow systems, material and liquid density calculations go hand-in-hand.
Sample Use Case
Imagine you’re an HVAC engineer installing a 12-foot copper pipe:
- Inner Diameter: 2 inches
- Length: 12 feet = 144 inches
$$Volume=π×(1)2×144≈452.39 cubic inches\text{Volume} = \pi \times (1)^2 \times 144 ≈ 452.39 \text{ cubic inches}Volume=π×(1)2×144≈452.39 cubic inches
Convert to gallons: 452.39231≈1.96 gallons\frac{452.39}{231} ≈ 1.96 \text{ gallons}231452.39≈1.96 gallons$$
This ensures that the system holds nearly 2 gallons, which is critical when calculating water weight and pressure head.
Pipe Volume in Flow Rate Calculations
Once volume is known, flow rate can be calculated using: $$Flow Rate=VolumeTime\text{Flow Rate} = \frac{\text{Volume}}{\text{Time}}Flow Rate=TimeVolume$$
Useful in applications where pipe systems must move water or fluid over specific time intervals, especially in irrigation, chemical processing, and hydraulics.
Pipe Volume FAQs
Q: Can I use the outer diameter to calculate volume?
A: Only if you subtract wall thickness to get the inner diameter.
Q: How accurate is this method?
A: Extremely accurate, provided you use correct measurements and consistent units.
Q: Does pipe material affect volume?
A: No, but it affects weight and structural integrity.
Q: What units does the pipe volume calculator support?
A: Cubic inches, feet, meters, gallons, liters, and more.
Q: Can it be used for gas pipes?
A: Yes, but include pressure and compressibility factors for gases.
Summary Table: Pipe Volume Calculator Inputs & Outputs
| Input | Unit Options | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Diameter | Inches, mm | Defines pipe cross-section |
| Pipe Length | Feet, meters, inches | Length of the pipe |
| Wall Thickness | Inches, mm | Needed if only outer diameter |
| Volume Output | Cubic inches/feet/meter | Internal pipe volume |
| Flow Rate | GPM, LPM | Movement of fluid per minute |
| Weight Output | Pounds, kg | Fluid weight inside pipe |
Final Thoughts
The Pipe Volume Calculator simplifies complex math so you can focus on the job. Whether you’re managing water in a residential plumbing system, designing HVAC ducts, or building an industrial pipeline, accurate pipe volume calculations are the foundation of reliable work. Used alongside tools like the ramp calculator, stair calculator, and other General Construction Calculators, it ensures every measurement is precise and every project stays on track.
From pipe diameter to flow rate, from cubic feet to gallons, and from liquid weight to volume capacity, this tool gives you the confidence to build efficiently.
