Free Schedule Variance Calculator Online
In project management, time is everything. Projects that fall behind schedule cost money, cause delays in deliverables, and impact overall productivity. That’s why tools like the schedule variance calculator are vital for project managers who want to keep their timelines on track. Using Construction Calculators gives you a precise look at how your project is performing compared to the planned schedule. Whether you’re managing a construction job, software rollout, or any other timed deliverable, understanding schedule variance allows you to make informed, timely decisions.
Schedule Variance Calculator
What Is Schedule Variance?
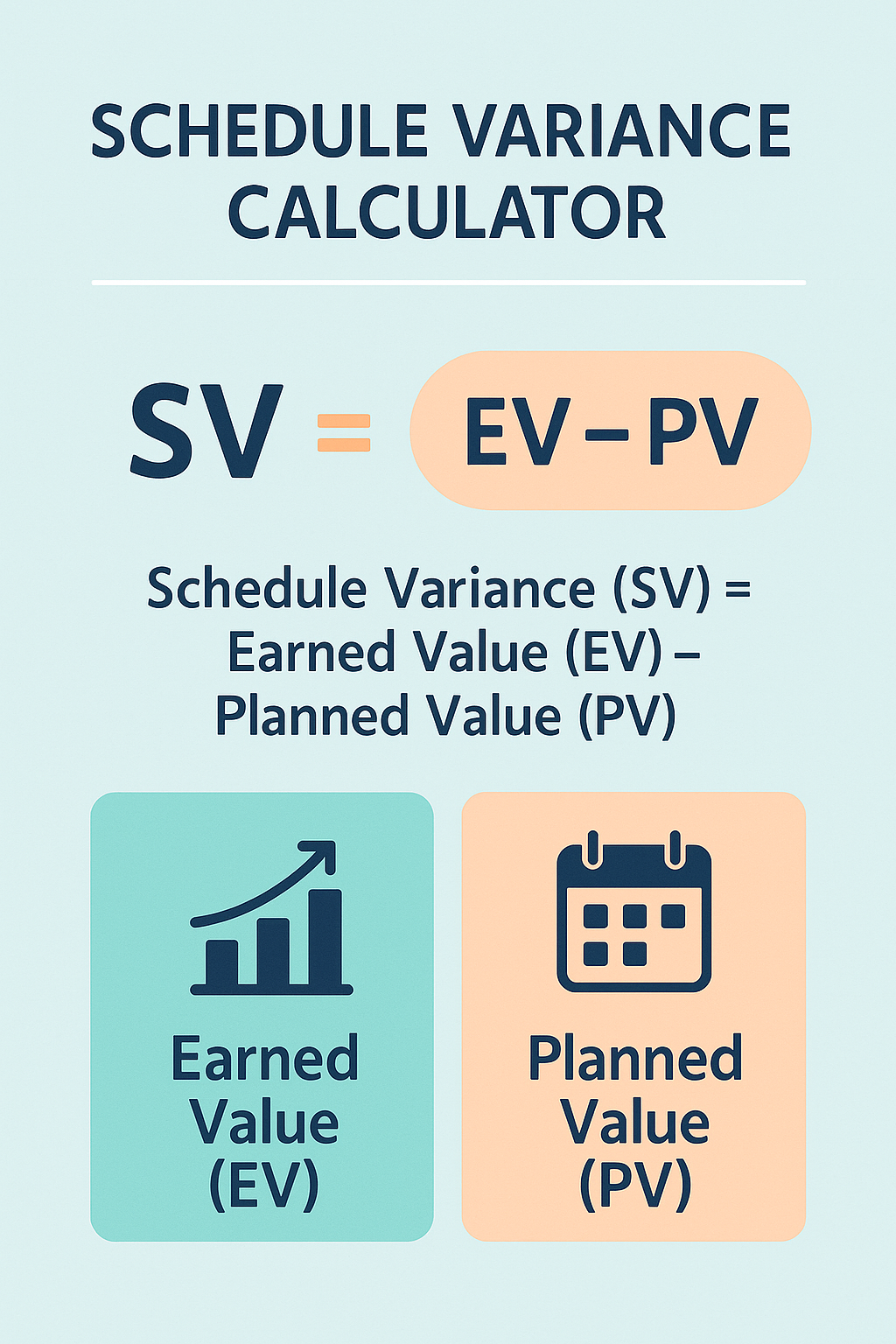
Schedule variance (SV) is a key metric in Earned Value Management (EVM). It tells you whether a project is ahead, behind, or exactly on schedule by comparing the amount of work planned to the amount of work actually completed at a specific point in time. The value is usually expressed in cost units, such as dollars, and is calculated using simple formulas based on planned value and earned value. Schedule Variance $$\text{Schedule Variance (SV)} = \text{Earned Value (EV)} – \text{Planned Value (PV)}$$
Where:
- EVEVEV = Earned Value, the budgeted cost of work actually performed
- PVPVPV = Planned Value, the budgeted cost of work scheduled to be performed
The result can be:
- Positive SV: Project is ahead of schedule
- Negative SV: Project is behind schedule
- Zero SV: Project is exactly on schedule
Why Use a Schedule Variance Calculator?
A schedule variance calculator automates the formula, reducing human error and saving time. This is especially useful on large projects where manual calculation across dozens of tasks is inefficient. The calculator takes inputs like EV and PV and provides an instant result that helps in reporting, forecasting, and corrective planning.
Using the calculator helps:
- Track actual progress against the schedule
- Communicate delays or accelerations clearly
- Make data-driven decisions quickly
- Ensure transparency with stakeholders
- Prevent schedule slippage and budget overflow
Understanding Earned Value and Planned Value
Earned Value (EV)
Earned Value represents the value of the actual work completed so far. It is calculated using the percentage of the completed work multiplied by the total project budget. EV = \text{Total Budget} \times \text{Actual % Complete}
Example: If the project budget is $100,000 and the team has completed 40% of the work, then EV=100,000×0.4=40,000EV = 100,000 \times 0.4 = 40,000EV=100,000×0.4=40,000
Planned Value (PV)
Planned Value is the value of the work that should have been completed according to the schedule by a certain point. PV = \text{Total Budget} \times \text{Planned % Complete}
Example: If your schedule says 50% of the project should be completed, then $$PV=100,000×0.5=50,000PV = 100,000 \times 0.5 = 50,000PV=100,000×0.5=50,000$$
Now, calculating schedule variance: $$SV=EV−PV=40,000−50,000=−10,000SV = EV – PV = 40,000 – 50,000 = -10,000SV=EV−PV=40,000−50,000=−10,000$$
This means your project is $10,000 behind schedule.
Other Supporting Formulas
To provide a more complete picture, project managers also use the Schedule Performance Index (SPI), which shows efficiency in schedule performance: Schedule Performance Index (SPI)=EVPV\text{Schedule Performance Index (SPI)} = \frac{EV}{PV}Schedule Performance Index (SPI)=PVEV
- SPI > 1.0 means ahead of schedule
- SPI < 1.0 means behind schedule
- SPI = 1.0 means on schedule
This index can be used along with the schedule variance calculator to enhance reporting and decision-making.
When to Use a Schedule Variance Calculator
Use the schedule variance calculator during:
- Weekly or monthly project reviews
- Earned Value Management reporting
- Stakeholder updates
- Risk assessments
- Contract performance evaluations
In Agile or iterative development models, SV can be tracked at the sprint or milestone level to make sure short cycles stay on target.
Benefits of Automating the Schedule Variance Calculation
Manually calculating schedule variance can work for small projects, but larger endeavors require automation for several reasons:
- Consistency: Ensures the same method is applied across all departments
- Speed: Provides real-time data
- Accuracy: Minimizes human error
- Transparency: Keeps all team members aligned
- Adaptability: Allows updates as the project progresses
With a calculator, users can input Earned Value and Planned Value in real time and receive instant results without dealing with spreadsheets or manual errors.
Real-World Example
Let’s say you are managing a project with a total budget of $200,000. After 10 weeks into the project, the following data is available:
- Planned work completion: 60%
- Actual work completed: 45%
Step 1: Calculate PV $$PV=200,000×0.6=120,000PV = 200,000 \times 0.6 = 120,000PV=200,000×0.6=120,000$$
Step 2: Calculate EV $$EV=200,000×0.45=90,000EV = 200,000 \times 0.45 = 90,000EV=200,000×0.45=90,000$$
Step 3: Calculate SV $$SV=EV−PV=90,000−120,000=−30,000SV = EV – PV = 90,000 – 120,000 = -30,000SV=EV−PV=90,000−120,000=−30,000$$
The negative result shows that the project is $30,000 behind schedule in terms of time-based work value.
Step 4: Calculate SPI $$SPI=EVPV=90,000120,000=0.75SPI = \frac{EV}{PV} = \frac{90,000}{120,000} = 0.75SPI=PVEV=120,00090,000=0.75$$
This means the team is working at 75% of the expected pace.
How to Interpret Results
Interpretation of the schedule variance value helps project managers create an action plan.
- SV = 0: No delay. The project is on schedule.
- SV > 0: The project is progressing faster than planned. Consider reviewing scope and adjusting future workload.
- SV < 0: There is a delay. Mitigation strategies should be implemented immediately.
Likewise, SPI shows whether the team is performing at, below, or above expected productivity. These numbers can then be compared to cost variance (CV) for a full picture of project health.
Applications Across Industries
Schedule variance calculators are widely used in:
- Construction Projects: Foundation work, installations, inspections
- IT and Software Development: Sprint management, release planning
- Manufacturing: Production cycles, machine output scheduling
- Event Management: Planning, vendor coordination, task dependencies
- Marketing Campaigns: Timelines for content delivery, ad launch
- Government Contracts: Milestone adherence and compliance metrics
No matter the field, controlling schedule deviation is critical to success.
What to Do if You’re Behind Schedule
If your schedule variance is negative, here are some steps to regain control:
- Reallocate resources to high-priority tasks
- Increase manpower or overtime if budget allows
- Cut scope (if possible) to meet time constraints
- Improve communication and accountability
- Update stakeholders with revised timelines
The key is timely reaction, and a schedule variance calculator gives you that visibility before it’s too late.
How Schedule Variance Fits into EVM
Schedule Variance is just one part of Earned Value Management (EVM), a broader framework that tracks cost, schedule, and scope performance. Other core EVM metrics include:
- Cost Variance (CV)
- Cost Performance Index (CPI)
- Estimate at Completion (EAC)
- To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI)
Together with SV, these metrics provide a full dashboard for project control. Many modern EVM tools come with built-in calculators for each metric, streamlining project management.
Summary: Why Schedule Variance Calculation Matters
A schedule variance calculator helps you:
- Quantify progress accurately
- Spot delays early
- Plan corrective actions
- Communicate more clearly
- Keep complex projects under control
It’s not just about tracking numbers it’s about making data-driven decisions in real time. Whether you manage construction, software, marketing, or any timed project, using the calculator gives you the confidence to lead effectively.
Conclusion
Managing project timelines without proper measurement is like driving without a speedometer. A schedule variance calculator provides that crucial insight, showing where you are, how fast you’re going, and whether you’re on track. It helps detect delays early, empowers decisions, and prevents schedule slippage before it causes bigger issues. With accurate inputs like Earned Value and Planned Value, and essential formulas built in, this tool becomes an asset for any serious project leader. Invest the time in understanding and using schedule variance calculations—alongside tools like the General Construction Calculators, Tank Volume Calculator, and Stair Calculator—and watch your project timelines stay in sync with your plans.
