Free Welding Rod Consumption Calculator Online
In any welding project, precision starts with preparation. Estimating the right quantity of welding rods not only saves material costs but also ensures consistent weld quality across jobs. That’s where a welding rod consumption calculator becomes an essential tool. It allows fabricators, welders, and project managers to calculate the total welding electrode requirement based on key project variables—weld length, joint type, electrode diameter, and deposition efficiency—using Construction Calculators to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Whether you’re working on a structural steel frame, pipeline, or sheet metal fabrication, understanding your welding rod consumption helps optimize production schedules, reduce waste, and enhance operational efficiency.
Welding Rod Consumption Calculator
What Is a Welding Rod Consumption Calculator?
A welding rod consumption calculator is a practical tool used to estimate how many welding electrodes will be required to complete a given welding job. It factors in weld dimensions, filler metal type, rod diameter, deposition rate, and sometimes welding process specifics like stick (SMAW), MIG, or TIG welding.
It’s especially useful for:
- Procurement planning
- Budget estimation
- Project scheduling
- Reducing leftover electrode stock
- Avoiding mid-job material shortages
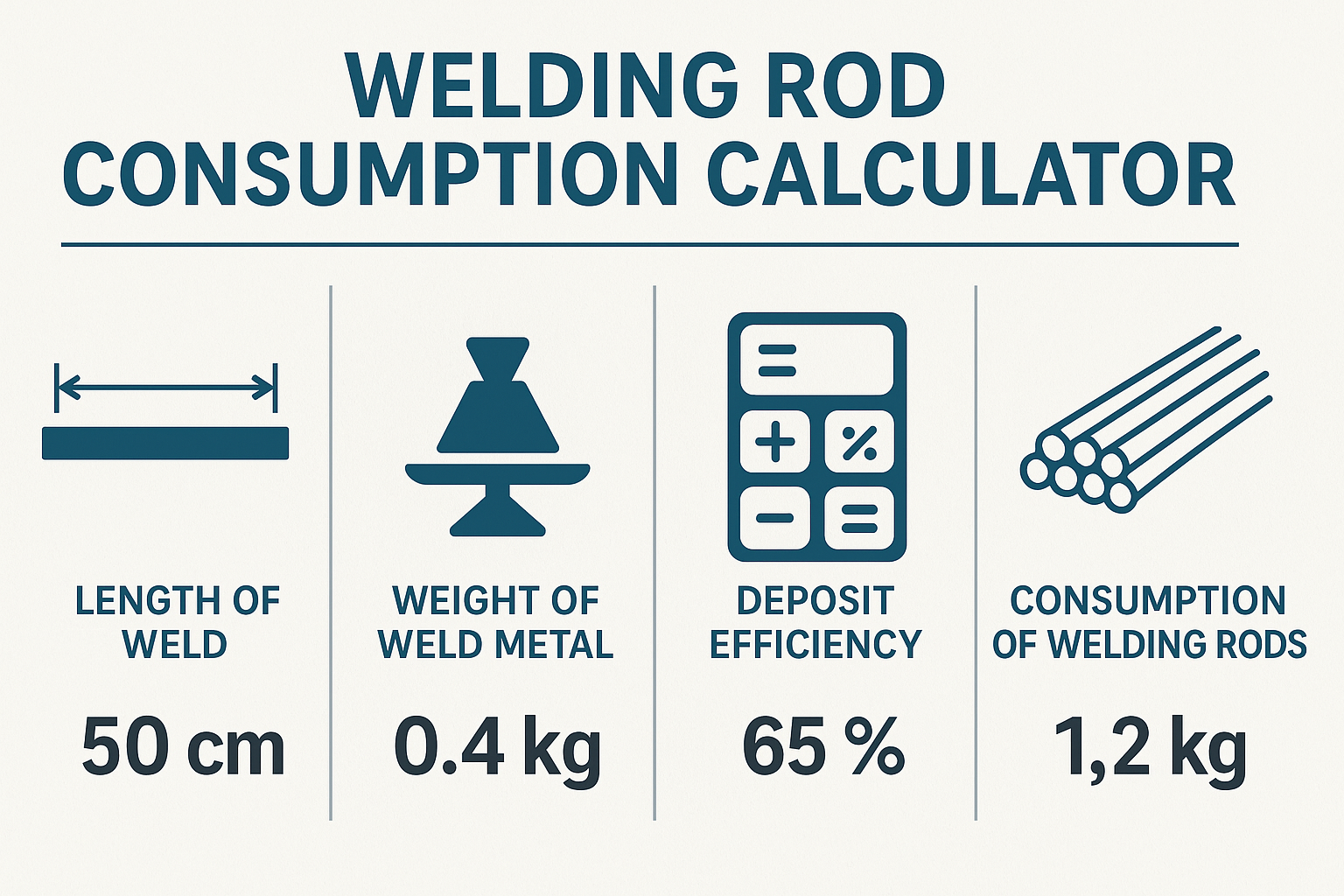
Key Inputs for the Calculator
To calculate welding rod consumption accurately, you’ll need the following inputs:
- Total weld length (meters or feet)
- Weld type (fillet, butt, groove)
- Weld size (leg length or throat size)
- Electrode diameter
- Deposition efficiency (typically 60%–85% depending on electrode type)
- Type of material (mild steel, stainless, etc.)
- Welding process (SMAW, GMAW, FCAW)
Each of these factors contributes to the estimated weight and number of rods required. Some calculators also allow you to specify vertical or overhead welding positions that affect deposition efficiency.
Why Estimating Welding Rod Consumption Matters
Overestimating rod consumption leads to inflated project costs and unnecessary material inventory. Underestimating creates interruptions and delays on-site. Both scenarios affect productivity and welding quality. A good welding rod consumption calculator eliminates guesswork by providing a material list based on actual weld geometry and technical parameters. It’s particularly valuable for large-scale fabrication jobs, offshore structures, shipbuilding, bridges, and plant maintenance work.
Common Welding Rod Types and Their Properties
Welding rods or electrodes are classified by AWS standards. Some of the most common include:
- E6010: Deep penetration, fast-freeze rod, ideal for pipelines and root passes
- E6013: All-purpose, used for thin metals and sheet welding
- E7018: Low hydrogen, high-strength, excellent for structural welding
- E7024: High deposition rate, used in flat and horizontal positions
Each electrode type has a unique weight, burn-off rate, and deposition efficiency, all of which are crucial in calculating consumption.
Welding Rod Weight Estimation Formula
A simplified version to estimate the weight of weld metal required is: $$\text{Weld Metal Weight (kg)} = L \times A \times \rho$$
Where:
- LLL = Total weld length (in meters)
- AAA = Cross-sectional area of weld bead (in cm²)
- ρ\rhoρ = Density of the weld metal (~7.85 g/cm³ for carbon steel)
Once the total weld metal weight is known, you can calculate the number of electrodes required.
Formula to Calculate Number of Welding Rods
$$Number of Rods=WmD×η\text{Number of Rods} = \frac{W_m}{D \times \eta}Number of Rods=D×ηWm$$
Where:
- WmW_mWm = Weld metal weight (in kg)
- DDD = Weight deposited per rod (kg/rod)
- η\etaη = Deposition efficiency (decimal form, e.g., 0.65 for 65%)
This formula helps you convert total weld metal volume into electrode count based on burn-off weight and efficiency.
Example Calculation
Let’s assume:
- Weld length = 15 meters
- Fillet weld with 6 mm leg size
- Cross-sectional area (A) = 0.21 cm²
- Density = 7.85 g/cm³
Then: $$Wm=15×0.21×7.85=24.72 kgW_m = 15 \times 0.21 \times 7.85 = 24.72 \text{ kg}Wm=15×0.21×7.85=24.72 kg$$
Assuming:
- Weight per rod = 0.12 kg
- Deposition efficiency = 0.65
$$Number of Rods=24.720.12×0.65≈317 rods\text{Number of Rods} = \frac{24.72}{0.12 \times 0.65} \approx 317 \text{ rods}Number of Rods=0.12×0.6524.72≈317 rods$$
This means approximately 317 electrodes would be needed for the entire weld.
Deposition Efficiency by Electrode Type
| Electrode Type | Deposition Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
| E6010 | 55–65% |
| E6013 | 60–70% |
| E7018 | 70–80% |
| E7024 | 85–90% |
Selecting the right electrode can directly impact material savings. Higher efficiency means fewer rods and less time spent changing electrodes.
Welding Process Variations
Each welding process changes the rod or wire usage:
- SMAW (Stick Welding): Uses covered electrodes; most commonly calculated with rod consumption.
- GMAW (MIG): Uses continuous wire feed; consumption calculated in kg per meter.
- FCAW: Similar to MIG but uses flux-cored wire; wire feed rates affect consumption.
- TIG (GTAW): Uses filler rod manually fed into the arc; slower deposition rate.
This guide focuses on stick electrodes (SMAW), but the calculator concept extends to other processes with wire feed rate adjustments.
Using the Calculator for Procurement
Welding projects often span weeks or months, especially in industries like shipbuilding, pressure vessel fabrication, and heavy machinery. Using a welding rod consumption calculator allows procurement teams to:
- Order the exact quantity needed
- Avoid overstocking and underutilization
- Coordinate material delivery schedules with project milestones
- Allocate budget more accurately
Procurement staff can also set usage thresholds and reorder points based on consumption predictions from the calculator.
Field Application and Adjustments
Welding is rarely performed under perfect lab conditions. Field conditions may reduce deposition efficiency due to:
- Wind in outdoor welding
- Overhead or vertical positions
- Contaminated surfaces
- Inconsistent weld speed
The calculator should allow for adjustment coefficients, typically reducing efficiency by 5–15% depending on environment. You may include a correction factor: $$Adjusted Rods=Number of Rods×(1+Loss Factor)\text{Adjusted Rods} = \text{Number of Rods} \times (1 + \text{Loss Factor})Adjusted Rods=Number of Rods×(1+Loss Factor)$$
Example: 317 rods × (1 + 0.10) = 348 rods (rounded)
Benefits of a Welding Rod Consumption Calculator
Using a calculator delivers multiple operational benefits:
- Accurate weld planning
- Lower material waste
- Fewer delays due to rod shortage
- Better quality control from consistent welding
- Lower inventory holding cost
- Stronger project documentation and compliance
It also boosts project tracking by creating measurable estimates tied to weld progress.
Welding Rod Calculator in Software Tools
Modern fabrication software, ERP systems, and mobile apps now integrate welding rod calculators. These digital solutions allow:
- Weld log tracking
- QR code material scanning
- In-field data entry by welders
- Real-time updates for procurement
Some calculators even include metal selection, weld joint library, weld pass simulation, and productivity tracking.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this calculator for MIG or TIG welding?
Yes, but the units change to wire weight or rod length rather than stick count.
Q: Do different rod brands affect consumption?
Slightly. Weight per rod and burn rate can vary, but the calculator accounts for standard averages.
Q: What if the weld is multi-pass?
Calculate the total volume per pass and multiply by the number of passes.
Q: How do I know the weld cross-section?
Refer to design specs or use standard weld size tables.
Q: Does slag count as deposited metal?
No. Only metal fused into the joint is considered deposited weight.
Conclusion
Welding rod consumption calculators are powerful tools that bridge the gap between design planning and on-site execution. From reducing excess inventory to ensuring job site readiness, they streamline every phase of a welding project. Whether you’re a shop foreman, project engineer, or procurement manager, using a welding rod calculator improves cost control, precision, and efficiency. Tools like General Construction Calculators, construction calculator osrs, and the Taper Calculator support better forecasting and smoother operations across all welding applications.
With clear formulas, real-time adaptability, and room for field-based corrections, you can manage your welding material needs with confidence. Start by entering your weld specs, and let the calculator do the work because in welding, every rod counts.
